Cryptology

Encryption

Modes of Operation
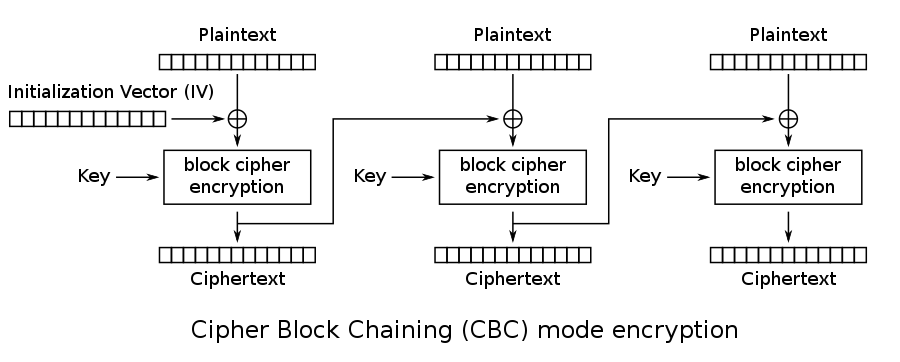
There are various modes of operation designed to apply the cryptographic algorithm (especially block cipher) to enhance confidentiality, e.g., Cipher block chaining (CBC), Cipher Feedback (CFB), Output Feedback (OFB), Counter (CTR), etc.
Please refer to CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20220103 for more.
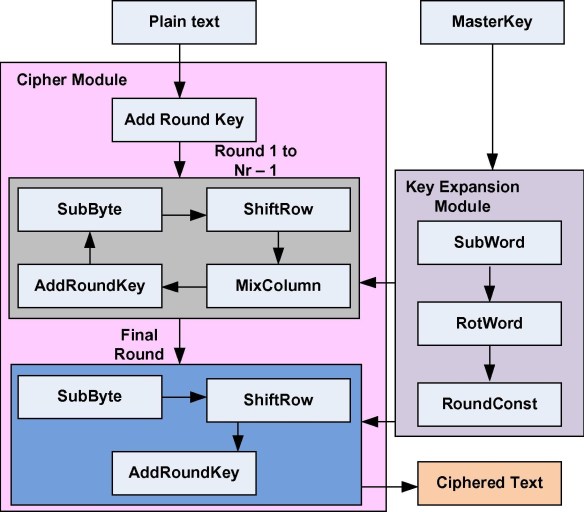
Standard Overview of AES algorithm
In the AES Proposal: Rijndael, it reads:
In most ciphers, the round transformation has the Feistel Structure. In this structure typically part of the bits of the intermediate State are simply transposed unchanged to another position. The round transformation of Rijndael does not have the Feistel structure. Instead, the round transformation is composed of three distinct invertible uniform transformations, called layers. By “uniform”, we mean that every bit of the State is treated in a similar way.
Please refer to CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20211112 for more.
Key Generation and Entropy
It’s common that symmetric ciphers nowadays typically employ a secret key with a length between 128 and 256 bits. Block ciphers use fixed-length keys, while stream ciphers use a fix-length key to generate a keystream that works like a conveyor belt and looks unlimited.
Entropy is a measure of the disorder, randomness, or variability in a closed system. An entropy value is between 0 and 1. The higher an entropy value is, the more unpredictable a key generator is.
Please refer to CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20220119 for more.



RSA (cryptosystem)
RSA is a public-key cryptosystem, published in 1977 by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman. A public key is generated based on two large prime numbers. Even though the public key is shared publicly, the two large prime numbers shall be kept secret.

Please refer to CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20210715 for more.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. (Wikipedia)
In cryptography, PKCS stands for “Public Key Cryptography Standards”. These are a group of public-key cryptography standards devised and published by RSA Security LLC, starting in the early 1990s. (Wikipedia)
Please refer to the following links for more:
- CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20201018
- CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20210203
- CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20211227



