Zero Trust is a Cybersecurity Paradigm for a Fine-grained, Dynamic, and Data-centric Access Control that supports visibility.
(Access control is mediating the usage of resources by authentication, authorization, and accounting based on the principles of need-to-know and least privileges.)
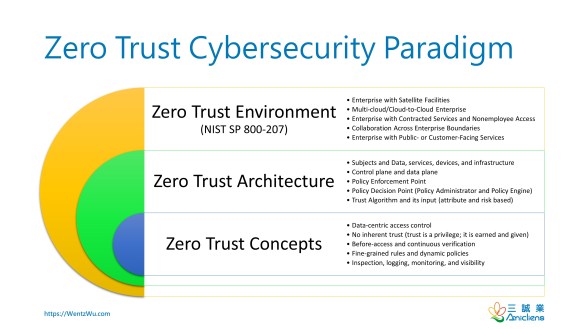
Zero Trust Cybersecurity Paradigm
The following diagram summarizes my study of Zero Trust that synthesizes various sources, such as Jericho Forum, DoD GIG/Black Core, Forrester’s Zero Trust Network, Google’s BeyondCorp, CSA’s SDP, and NIST SP 800-207.
Zero Trust Concepts
- Data-centric access control
- No inherent trust (trust is a privilege; it is earned and given)
- Before-access and continuous verification
- Fine-grained rules and dynamic policies
- Inspection, logging, monitoring, and visibility
Zero Trust Architecture
- Subjects and Data, services, devices, and infrastructure
- Control plane and data plane
- Policy Enforcement Point
- Policy Decision Point (Policy Administrator and Policy Engine)
- Trust Algorithm and its input (attribute and risk based)
John Kindervag and Zero Trust
John Kindervag coined Zero Trust in 2010 to eliminate the concept of “trust” that relies on perimeter security. He advocates that perimeter security is broken and not sufficient anymore and called the blind trust in network locations as “broken trust.” I believe “inherent authorization” is the core idea of “trust” in his Zero Trust Network Model and conclude his main idea of Zero Trust as follows:
Don’t rely on network locations (coarse-grained perimeters), but protect data and related resources (he called MCAP or microcore and perimeters) grouped into smaller pieces using an integrated segmentation gateway (NGFW, next-generation firewall).
Zero Trust Myths
He is now the field CTO of Palo Alto Networks. The company introduced Zero Trust Myths as follows:
- The goal of Zero Trust is to make a system trusted.
- It’s complex, costly and time-consuming.
- Zero Trust is all about identity.
- You can do Zero Trust at Layer 3.
I agree with all the myths but the first one, which treats “trust” as the synonym of “inherent authorization.” We don’t build systems that rely on inherent authorization, the so-called “trust” above, but I’d rather define trust as the confidence in security or trustworthiness. So, we do want to eliminate inherent authorization (blind/broken trust) to make a system trusted (secure and trustworthy), that is, to deliver a secure and trustworthy system and render assurance.
References
- NIST SP 800-207
- John Kindervag
- The Truth About Zero Trust (Palo Alto)
- Build Security Into Your Network’s DNA: The Zero Trust Network Architecture (Forrester)
- Department of Defense Global Information Grid (GIG) Architectural Vision
- BeyondCorp – A new approach to enterprise security (Google)
- Software Defined Perimeter (SDP) Architecture Guide (CSA))
- Zero Trust Architecture and Solutions (Gartner)


Pingback: CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20201022 - Wentz Wu
Pingback: 什麼是零信任(What is Zero Trust)? – Choson資安大小事